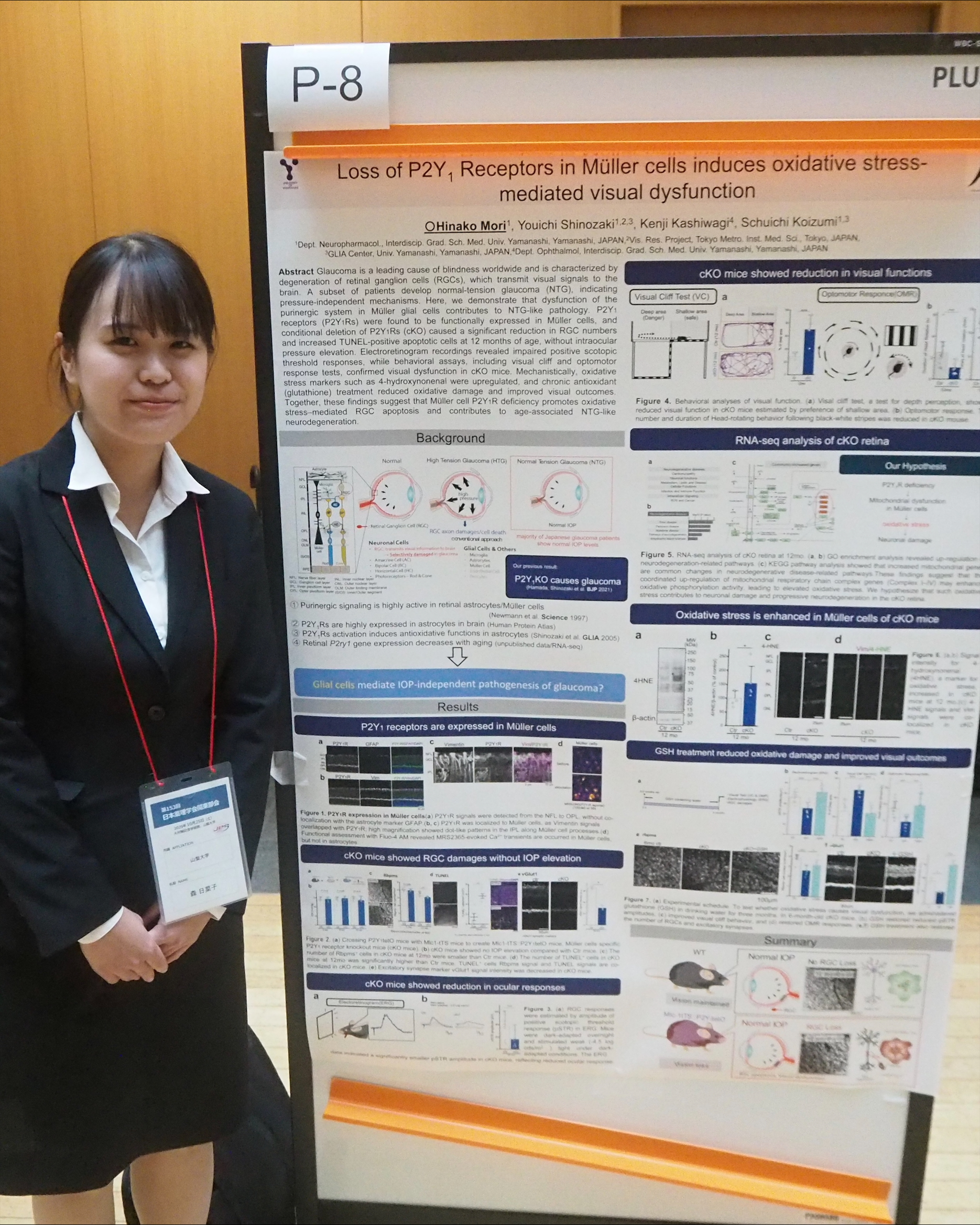
2025年10月25日に行われた第153回薬理学会関東部会に参加させていただきました。そこで「Loss of P2Y1 receptors in Müller cells induces oxidative stress-mediated visual dysfunction (ミューラー細胞のP2Y1受容体欠損は酸化ストレス依存的な視機能障害を誘導する)」というタイトルでポスター発表させていただきました。
発表では先生方からたくさんの質問、アイデアをいただきました。また、先生方の発表をお聞きして、多くの新たな知見を得ることができ、とても貴重な経験となりました。
今回の発表に関しましてご指導いただきました、小泉先生、篠崎先生を始めとする薬理学講座の先生方と、ご支援いただきましたライフサイエンスコース事務局の皆様にこの場を借りて心より感謝申し上げます。
以下が抄録となります。
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness, results from retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) degeneration, with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) as a key risk factor. However, but many Japanese patients develop normal-tension glaucoma (NTG), indicating pressure-independent mechanisms. We investigated P2Y1 receptors (P2Y1Rs), highly expressed in Müller glial cells and declining with age, using Müller cell-specific P2Y1R knockout (cKO) mice. At 12 months, cKO mice showed apoptotic RGC loss without IOP elevation, impaired retinal function and visual deficits. RNA-sequence analysis of cKO retina suggested an upregulation of oxidative stress, a major glaucoma risk factor, confirmed by elevated 4-hydroxynonenal signals. Chronic administration of glutathione mitigated this oxidative damage, protected RGCs, and restored visual function. These findings suggest that dysfunction of P2Y1Rs in Müller cells may represent a triggering mechanism for NTG through the induction of oxidative stress.